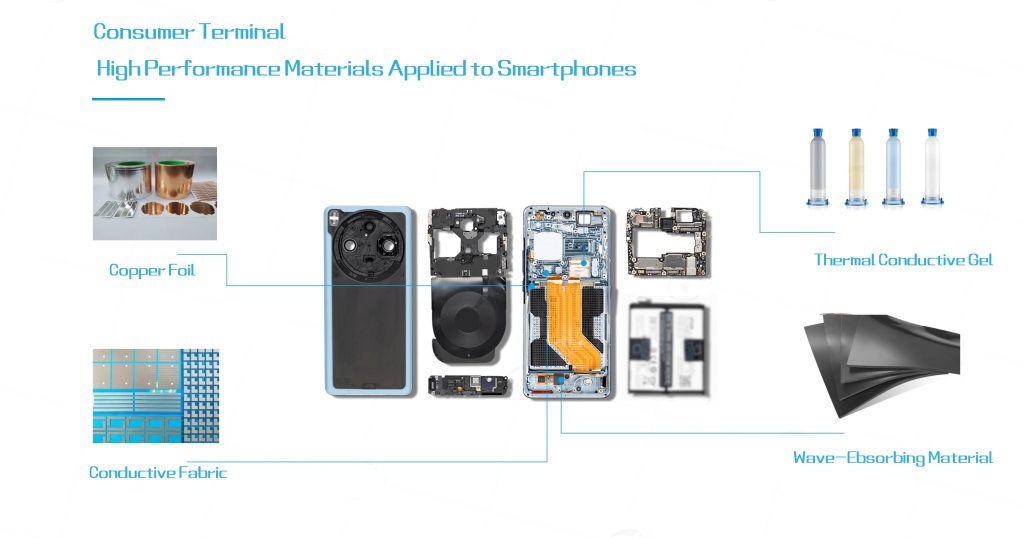
The relentless pursuit of thinner form factors and higher performance in smartphones has made thermal management and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) increasingly critical challenges. This article explores the strategic application of thermal gel, wave-absorbing materials, conductive fabric, and copper foil in modern smartphone design.
Thermal and EMC Challenges in Smartphones
Primary Heat Sources:
- Application processors (AP) and 5G modems
- High-frequency RF power amplifiers
- Camera modules and image signal processors
- Fast charging circuits and power management ICs
- Display drivers and graphics processing units
Critical Design Constraints:
- Ultra-thin profiles with z-heights under 8mm
- Metallic frames and glass backs limiting heat dissipation
- High-density component placement
- Stringent signal integrity requirements for 5G/mmWave
Material Solutions for Smartphone Applications
1. Thermal Gel: Precision Thermal Interface Solution
Critical Applications:
- Between application processor and heat spreader/ vapor chamber
- Camera module interfaces requiring maximum thermal performance
- 5G modem chipsets and RF front-end modules
- Areas with microscopic surface variations and minimal gap tolerance
Performance Advantages:
- Ultra-low thermal resistance through perfect surface wetting
- Excellent performance in vibration-prone mobile environments
- Automated dispensing compatibility for high-volume manufacturing
- Superior long-term stability without pump-out or dry-out
2. Wave-Absorbing Materials: EMI and Thermal Integration
Strategic Applications:
- 5G antenna modules and mmWave arrays
- High-speed memory interfaces (LPDDR5/5X)
- Camera flex cable interfaces and display connectors
- Near-field communication (NFC) and wireless charging coils
Multifunctional Benefits:
- Suppresses electromagnetic interference at specific frequency bands
- Provides secondary thermal dissipation path
- Enhances signal integrity for high-speed data transmission
- Redoves cavity resonance in compact enclosures
3. Conductive Fabric: Flexible Shielding Solutions
Implementation Areas:
- Display module shielding and grounding
- Camera module electromagnetic containment
- Battery interface shielding and flex cable protection
- Internal compartment isolation between RF sections
Key Features:
- Excellent flexibility for complex 3D formations
- Low compression force for delicate components
- Consistent surface contact for reliable grounding
- Tear-resistant properties for automated installation
4. Copper Foil: High-Performance Shielding and Thermal Spreading
Critical Applications:
- Localized heat spreading for processor areas
- High-frequency shielding for 5G antenna modules
- Flexible printed circuit (FPC) electromagnetic protection
- Battery management system shielding
Technical Advantages:
- Superior thermal conductivity for heat spreading applications
- Excellent high-frequency shielding effectiveness
- Thin profiles (8-25μm) suitable for tight spaces
- Die-cut capability for precision applications
Integrated Implementation Strategy
Thermal Management Hierarchy:
- Thermal gel for primary heat sources (AP, 5G modem)
- Copper foil for secondary heat spreading and local thermal management
- Wave-absorbing materials providing supplemental thermal paths
EMI Control Framework:
- Conductive fabric for large-area shielding and grounding
- Copper foil for high-frequency localized protection
- Wave-absorbing materials for specific frequency suppression
Performance Optimization
Thermal Performance:
- Maximum interface performance through thermal gel application
- Efficient heat spreading using copper foil layers
- Comprehensive thermal pathway design from chip to chassis
EMI Control:
- Multi-layer shielding approach using complementary materials
- Frequency-specific absorption for critical RF circuits
- Comprehensive grounding strategy throughout assembly
Manufacturing Considerations
Production Compatibility:
- Automated dispensing systems for thermal gel application
- Precision die-cutting for fabric and foil components
- High-speed placement equipment for shielding materials
- Rework capability for service and repair scenarios
Quality Assurance:
- Consistent thermal interface thickness control
- Shielding material adhesion and contact reliability
- Long-term performance validation under thermal cycling
- Environmental testing for humidity and mechanical stress
Conclusion
The sophisticated integration of thermal gel, wave-absorbing materials, conductive fabric, and copper foil enables smartphone manufacturers to achieve the delicate balance between thermal performance, electromagnetic compatibility, and form factor requirements. As smartphones continue to evolve with more powerful processors and advanced 5G capabilities, the strategic deployment of these advanced materials becomes increasingly critical for delivering devices that meet both performance expectations and regulatory requirements.
Manufacturers who master the coordinated application of these material solutions will lead the industry in producing smartphones that excel in thermal management, signal integrity, and overall user experience. The future of smartphone innovation will increasingly depend on these advanced material technologies to overcome the physical limitations of smaller form factors and higher performance demands.